Application of Remote Sensing for Large area Estimation
Estimating forest carbon balance by remote sensing
The Center for Global Environmental Research (CGER) uses remote sensing to estimate carbon balance in a forest ecosystem and develop related methodology. Satellite- or air-borne remote sensing techniques are one of the useful tools to scale up the information from a small area, such as that derived from eddy covariance CO2 flux observations. The use of remote sensing is expected to grow and expand as it provides convenient means to monitor forest continuously and non- invasively, replacing the more common labor-intensive investigation methods.

Observation
We monitor solar, photosynthetically active radiation and vegetation indices using remote sensing techniques at the Fujihokuroku and Teshio sites. Also, we aim to develop and improve the observation techniques using automated digital cameras installed on observation towers to ascertain physiological activity changes.
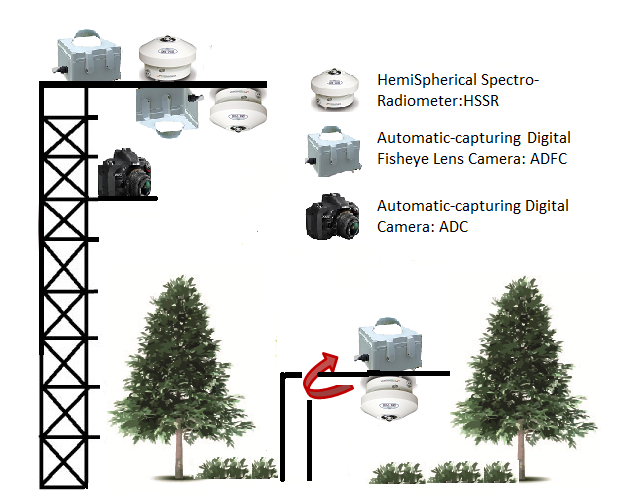
Phenology
Phenology is the scientific study of periodic biological phenomena, such as germination, leaf expansion, flowering, breeding, leaf coloration and leaf fall, in relation to climatic conditions. Recent climate change has notable effects on the timing of phenology, such as change in the timing of leaf expansion and coloration. Plant phenology is an indicator of not only climate change effects, but also associated carbon exchanges and atmospheric CO2 concentrations
Fujihokuroku site

*Phenological photographs of Fujihokuroku larch forest by fisheye lens camera
*Please visit PEN(Phenological Eyes Network)HP for daily observation results obtained by fisheye lens camera.
Teshio site

Tomakomai site after 2004




